Back صدر الدجاجة (نجم) Arabic Sadr AST Sadr Catalan Sadr (Stern) German Σαντρ Greek Sadr Spanish Sadr Basque صدرالدجاجه Persian Gamma Cygni Finnish Gamma Cygni French
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 20h 22m 13.70184s[1] |
| Declination | +40° 15′ 24.0450″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 2.23[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F8 Iab[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.54[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.67[2] |
| Variable type | suspected[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | -7.5[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +2.39[1] mas/yr Dec.: -0.91[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 1.78 ± 0.27 mas[1] |
| Distance | approx. 1,800 ly (approx. 560 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −4.54[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 14.5±1.1[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 183[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 33,023[9] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.02±0.10[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 5,790±100[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.02[6] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 15[10] km/s |
| Age | 12[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
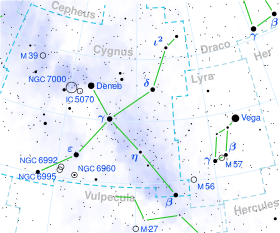
Gamma Cygni (γ Cygni, abbreviated Gamma Cyg, γ Cyg), officially named Sadr /ˈsædər/,[11][12] is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, forming the intersection of an asterism of five stars called the Northern Cross. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 1,800 light-years (560 parsecs) from the Sun.[1]
It forms the primary or 'A' component of a multiple star system designated WDS J20222+4015 (the secondary or 'BC' component is CCDM J20222+4015BC, a close pair of stars 40" away from γ Cygni[13]).
- ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
aaa474_2_653was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
clpl4_99was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
aj140_5_1329was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
rgcrvwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Kovtyukh, V. V.; Gorlova, N. I.; Belik, S. I. (2012). "Accurate luminosities from the oxygen λ7771-4 Å triplet and the fundamental parameters of F-G supergiants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 423 (4): 3268–3273. arXiv:1204.4115. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.423.3268K. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21117.x. ISSN 0035-8711. S2CID 118683158.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
mnras402_2_1369was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
kalerwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
an331_4_349was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
coapa239_1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Kunitzsch, Paul; Smart, Tim (2006). A Dictionary of Modern star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations (2nd rev. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Pub. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.
- ^ "Naming Stars". IAU.org. Retrieved 1 March 2018.
- ^ "CCDM J20222+4015BC -- Double or multiple star", SIMBAD, Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg, retrieved 2018-03-01